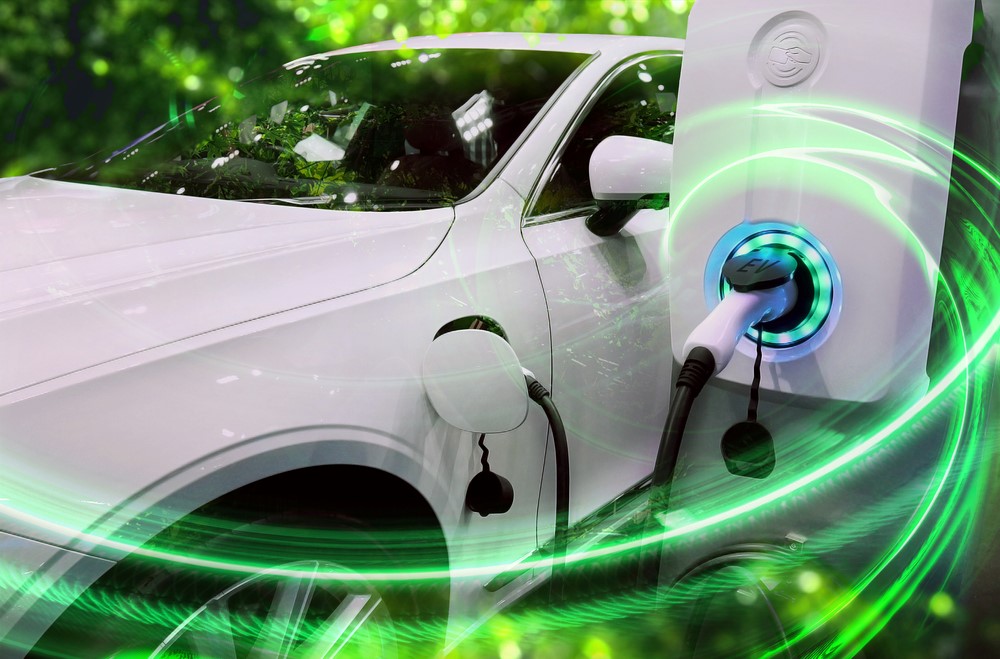
In a significant move towards sustainable transportation, Senegal has announced plans to implement a comprehensive regulatory framework to promote and regulate the use of electric vehicles (EVs). This initiative, unveiled by Minister of Infrastructure, Land, and Air Transport Malick Ndiaye on July 15, 2024, marks a pivotal step in the nation's commitment to environmental sustainability and modernization of its transport infrastructure.
Collaboration with Manufacturing Africa
To effectively establish this regulatory framework, Senegal is collaborating with Manufacturing Africa, a UK-based company specializing in industrial development. This partnership aims to leverage international expertise to create policies and mechanisms that encourage the adoption of electric vehicles among Senegalese citizens.
Development of a Master Plan for Transport Infrastructure
Alongside the regulatory framework, Senegal is developing a master plan for transport infrastructure, focusing on achieving multimodality between different types of transport, particularly in Dakar. This plan aims to reconfigure and modernize the nation's transport infrastructure, facilitating a seamless integration of various transportation modes and enhancing overall efficiency.
Minister Ndiaye's Vision for Electric Mobility
Minister Ndiaye emphasized the multifaceted benefits of transitioning to electric vehicles, stating that it would not only reduce costs but also positively impact the population by providing comfortable mass transportation with preferential rates. This vision aligns with global trends towards sustainable urban mobility and reflects Senegal's proactive approach to environmental challenges.
Economic and Environmental Implications
The adoption of electric vehicles is expected to have significant economic and environmental implications for Senegal:
- Economic Benefits:
- Reduced reliance on imported fossil fuels can lead to substantial savings and improve the nation's trade balance. Additionally, the development of a local EV industry could create job opportunities and stimulate economic growth.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to improved air quality and a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns with Senegal's commitments under international climate agreements and its national environmental policies.
Challenges and Considerations
While the initiative presents numerous benefits, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Infrastructure Development:
- Establishing a widespread and reliable network of charging stations is crucial for the success of electric vehicle adoption. This requires significant investment and strategic planning to ensure accessibility across urban and rural areas.
- Public Awareness and Acceptance:
- Educating the public about the benefits of electric vehicles and addressing concerns related to performance, cost, and maintenance are essential for widespread adoption.
- Policy and Incentives:
Implementing supportive policies, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and import duty reductions for electric vehicles and related components, can encourage both consumers and businesses to transition to electric mobility.
Regional Context and Potential
Senegal's initiative is part of a broader trend in West Africa towards embracing electric mobility. Countries in the region are exploring electric vehicles as a solution to fuel crises and environmental challenges. For instance, the adoption of electric vehicles has been proposed as a means to address fuel supply disruptions in West Africa, highlighting the potential for regional collaboration and shared learning.
Conclusion
Senegal's proactive approach to implementing a regulatory framework for electric vehicles, in collaboration with international partners, underscores its commitment to sustainable development and modernization of its transport infrastructure. By addressing the associated challenges and leveraging the potential benefits, Senegal is positioning itself as a leader in the transition to electric mobility in West Africa.